What is factoring?
Accounts receivable factoring (for that is its full name) is a service that allows you to sell invoices in exchange for cash. Factoring is used by those entrepreneurs who have not yet received money from their invoices. This is most often due to the long repayment period (of 60 days or 90 days, for example). In a situation where the company’s funds are thus “frozen” (the entrepreneur is waiting for the payment of several receivables at the same time), and there is a need to use them (the need to pay one’s own liabilities, an upcoming investment opportunity – there may be many reasons), the withheld funds are most easily recovered by opting for factoring.
The interested entrepreneur turns to a factoring company or bank offering a similar service for this purpose. The institution providing factoring is called a factor. The factor buys back from the factor (the entrepreneur using the factoring) its receivables and pays cash – usually within a few hours or a few days (depending on the type of factoring chosen and individual arrangements).
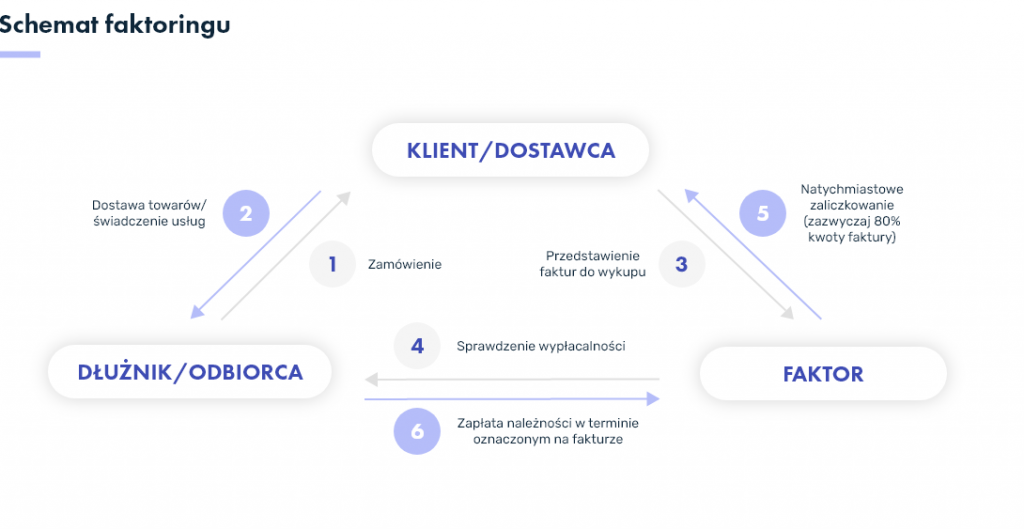
This is how – at the most basic level – the question can be answered: what is the definition of factoring and how does this type of service work? However, let’s remember that the financial services market must be prepared for a variety of situations, hence factoring itself has many varieties, of which the key is to choose the most appropriate one for a given company at a given time.
What are the types of factoring?
Most commonly, factoring is divided into two types – full factoring and incomplete fact oring. These two varieties differ from each other in important ways:
- Full factoring – otherwise known as factoring proper or non-recourse factoring – is a service in which the factor assumes full responsibility for the purchased receivable. The factor sells the invoice, receives the money and, to say the least, can forget about the matter. His contractor receives information regarding a change in the number of the account to which he must pay the money, and from now on he pays the amount due to the factor. In the event of any solvency problems, the collection of the receivables is handled by a factor.
- Incomplete factoring – improper factoring or factoring with recourse – is a variation of the service, in which it is the factoring company that uses factoring that must ensure that the counterparty repays its obligation on time. In the event of non-payment by the debtor, within the timeframe specified on the invoice, the factor is obliged to return the receivable received from the factoring company within the contractually specified timeframe.
- Mixed factoring – is a type of service that combines the features of full factoring and partial factoring. In practice, this means that the factor is liable for the insolvency of the factor’s counterparties up to the amount that is predetermined in the contract. Once the limit is exceeded, the liability shifts to the factor (i.e., it becomes de facto factoring with recourse).
For more on this topic, see the article Factoring – with or without recourse?
In addition to the aforementioned types, factoring can also be divided by several other criteria, including the institution that provides the financing, disclosure, territory, and scope of services. We will discuss all the aforementioned types of factoring in a little more detail later in the article.

Division by institution
Other varieties of factoring are bank factoring and non-bank factoring. As their names imply, this is an institution that can be used by a company wishing to finance its invoices.
The biggest difference between banks and factoring companies is in serving SME companies (a typical bank’s factoring client tends to be a large enterprise that boasts a richer credit history). In addition, banks place slightly more requirements on companies before they decide to provide factoring. Such practices are not used by factoring companies, which usually content themselves with analyzing the financial situation of debtors.
Further differences lie in the cost of the service (banks generally offer slightly lower factoring costs) and access to additional services (here, in turn, factoring companies win, offering a number of accompanying services as part of factoring, such as the redemption of individual invoices, accounts receivable processing or the ability to finalize factoring online).
Learn about additional services and the differences between factoring with a bank and with a factoring company by reading the article: Bank factoring vs. non-bank factoring .
Division by openness
By far the most popular form of factoring is open (open) factoring. In this case, the factoring company relies on transparency – its counterparty is informed of the factor’s assumption of the receivables by assignment. In this case, the state of the debtor’s finances is important – if it gets a positive rating, factoring becomes possible.
The inverse of this form is silent (secret or covert) factoring. In this scenario, the debtor does not find out that his creditor has taken advantage of factoring, so the receivable is transferred to the same account as usual.
An intermediate form is semi-open factoring, in which the debtor only learns of the sale of the receivable to the factoring company when he receives a pre-court demand for payment. In practice, this means that as long as he is not late with his payment, he will not find out about the change in the owner of the invoice at all.
For more on open factoring, see the article: Open factoring vs. silent factoring
.
Division by territory
In this specific category, we distinguish between domestic factoring and international factoring. Domestic factoring can only be used by companies registered and operating in Poland.
International factoring, on the other hand, is aimed at companies that do business abroad. This type of factoring is divided into two more: import and export factoring.
Import factoring can benefit companies that import goods from abroad into Poland, while export factoring can help businesses that sell their goods abroad maintain high liquidity.
For more information on international factoring , see the article International factoring – export and import factoring.
Division by scope of services
Some companies use factoring on a regular and permanent basis – this applies, for example, to companies that trade with foreign counterparties and issue invoices with exceptionally long repayment terms. It is for them that global (not to be confused with international) factoring will be the best solution.
Global factoring is a service in which the factor transfers to the factor all the invoices it issues to its counterparties. He submits them to the factoring agreement and then manages them, choosing which he wants to finance right away and which he leaves “in reserve.”
Single factoring is the inverse of global – it involves the transfer of one or more invoices to a factoring company. This is an ad hoc solution, useful for those companies that do not have liquidity problems on a daily basis, and need to release frozen funds on a one-time basis.
Other types of factoring available on the Polish market
The above-mentioned forms are among the most well-known and popular, but to get the full picture, it’s worth reviewing these less common forms of factoring as well.
Maturity factoring – is a specific type of factoring, in which the assumptions and purpose are different from the classic form. In this case, the factoring company is not concerned with maintaining liquidity or quickly raising funds for investment, but only with transferring the handling of receivables to the factoring company. After signing a maturity factoring agreement, the factor does not pay the factoring company – it will do so only after it has successfully raised money from the counterparty. This type of factoring is especially useful for those companies that do not have their own finance department or are unable to collect the money owed to them from their counterparty.
Reverse fact oring (commitment factoring) – is the literal inverse of the classic form of factoring. It is used by buyers, who in this way protect themselves against possible problems with the repayment of their debts. In this case, the company using factoring extends the time for itself to repay the obligation – before the due date passes, the factor transfers the money to the counterparty, and the buyer from then on is obliged to return the funds to the factoring company. Sometimes the company can get all sorts of bonuses in case of early repayment of debts. This is also one way to use reverse factoring.
Discount factoring – is a form of factoring that allows the company selling the service to receive funds immediately. There is a reason why another name for this type of service is expedited factoring. However, it is worth mentioning that the instant transfer of money is sometimes associated with a higher commission of the factor, which will realistically reduce the amount received.
Advance factoring – in this scenario, the factor, after entering into an agreement with the factor, only receives an advance payment, which is a percentage of the amount on the sales document, as specified in the agreement. The remainder of the receivable is paid only when the debtor settles the payment on the factor’s account.
Advantages and disadvantages of factoring
It is also worth mentioning the significant advantages and disadvantages of factoring. What makes it worth thinking about using just this financial service? What risks does it carry?
Disadvantages of factoring
Potential problems arising from the use of factoring include:
- Complicating communications between contractors by involving a third company;
- Handing over some of the financial decisions to another entity (although in some cases this can be an advantage);
- The risk of misunderstandings and damage to customer relations;
- The complexity of the service (some types of factoring are more complicated than others);
- not all entities, offering factoring service, work with smaller companies
Advantages of factoring
However, it is worth remembering that the factoring service also brings tangible benefits:
- The ability to gain immediate access to frozen funds;
- Improving the company’s liquidity and stabilizing revenues;
- Access to debt administration services;
- No burden on the company’s balance sheet (as opposed to lending);
- Factoring does not reduce creditworthiness;
- No need to secure claims;
- The ability to deduct financing costs from income tax and VAT;
- You can use the funds for any purpose – current expenses, payment of tax liabilities, or salaries for employees.
Which companies can benefit from factoring?
The answer to this question is very simple – virtually all of them. Banks’ factoring offerings are usually aimed at large companies. Non-bank institutions, on the other hand, mainly target micro, small and medium-sized enterprises. To be eligible for factoring, a company must settle with its counterparties on a non-cash basis and issue invoices with deferred payment. This is basically the only necessary condition to be met.
Most institutions finance invoices regardless of what industry the company is in. Due to distant payment terms, factoring is particularly popular in the transportation, construction, manufacturing and HoReCa industries. However, it is also perfect for services and trade.
As you can see, almost any company can benefit from factoring. In particular, however, it should be of interest to all those companies that:
- have problems maintaining liquidity by issuing invoices with distant payment dates;
- want to attract new contractors by being able to offer longer payment terms;
- are looking for alternative methods of financing the company;
- due to their short tenure, lack of credit history or low level of turnover, they cannot count on getting financing from a bank;
- are planning to increase sales/operations and are looking for a solution that will allow them easy access to current cash.
How much does a factoring service cost?
We already know what factoring is, what types of factoring there are, we know the benefits and drawbacks, and we know which companies should use it. It’s time to find out the cost. Several factors affect the price an entrepreneur will have to pay for factoring services. The most important of these is the type of service chosen. For example – the cost of undisclosed factoring, will be much higher than in the case of overt factoring, due to the risk that the factor assumes. Costs are also different for global factoring than for single factoring. Costs in PragmaGO can be calculated individually – priced per invoice (in the case of single factoring) or as a lump sum (with a fixed contract, in which the cost is one fixed monthly fee depending on the limit level).
Typically, the cost of factoring consists of two elements – the commission, which is the remuneration of the factor, and the interest on the advance granted for future payment of the invoice by the recipient. The commission usually varies between 0.2% and 3% per month. Interest, on the other hand, is largely based on the daily WIBOR rate and is charged for the entire period of use of the advance.
It is worth remembering that the cost of the service will most likely vary depending on the company providing the financing!
What a factoring agreement should contain
Before signing a factoring agreement, it is worth learning a little more about what should be included in such a document. A factoring agreement is an unfamiliar (mixed) contract, so you will not find a single template. Nevertheless, there are elements that must necessarily be included in such an agreement.
Among them are:
- The parties to the agreement (the factor and the factoring party. The debtor, although involved in the transaction, is not a party to the agreement);
- A detailed description of the claim (including: the value of the invoice, the date of payment, to whom it is due, who is the debtor, by what title and under what agreement it arises);
- Description of the rules under which the notification of the debtor about the change of ownership of the claim will take place;
- Type of factoring selected;
- Determination of the legal status of the claim;
- Payment terms and the amount of remuneration that the factor will receive from the factor;
- Determination of the entity responsible for the debtor’s insolvency;
- Legal safeguards.
For a contract to be legally binding, the signatures of both parties must appear on the document.
How to start working with a factoring company?
Depending on which factor you choose, the process may vary slightly. If you have decided on our offer, it is extremely easy to start working with us. All you have to do is choose the type of financing you are interested in – permanent (online factoring) or from time to time (invoice financing), and then fill out the corresponding application.
Permanent financing at PragmaGO
In the case of permanent financing, we will ask you to provide some data about your company and indicate your regular contractors, as well as the limit you want to apply for. If you are a sole proprietor, we will additionally ask you to provide your data and consent to BIK verification. You don’t have to worry, this approval, does not affect your BIK history in any way. The final step is identity verification, which can be done in two ways – by logging into your Kontomatik account or by a one-time verification transfer of PLN 1.
We will get back to you with a decision and terms of the agreement within 24 hours of sending the application. At that time you will also receive from us access to the Customer Area. Once you have signed the contract and the recipients have confirmed the assignment, you can conveniently submit invoices for financing and enjoy cash available in your account in an instant.
The maximum waiting time for cash is only 2 hours!
Remember that the limit you are given at the beginning can be reduced or increased over the course of the contract, if necessary. All you have to do is contact your caregiver and report your needs to him.
Have you ended cooperation with one of the recipients indicated in the application? Or maybe you want to add another one? It’s no problem at all! We focus on flexibility, so you are free to add and remove recipients at any stage of the contract.
Financing from time to time at PragmaGO
The process is slightly different for invoice financing, which can also be described as occasional or single financing. This type of factoring will also work well if you are considering permanent factoring, but are not completely convinced and want to test whether invoice financing is for you.
Here we will ask you at the very beginning to attach the invoice you want to sell to us. We will also need basic information about your company and your customer. If you have a sole proprietorship, as in the case of permanent factoring, you will be asked to provide the owner’s data. The last step is also to confirm your identity.
You will receive a financing decision from us within a maximum of two hours, and the funds for the invoice will hit your account with the first banking session, as soon as the recipient confirms the legitimacy of the invoice.
You no longer have to worry about liquidity. Whichever solution you decide on, you can receive the funds from the invoices you issue even on the same day, and your customers can still enjoy deferred payment terms. The only thing that changes for them is the account number to which they transfer funds. Long payment terms will no longer be a problem for your company.
Why choose factoring from PragmaGO?
- A flexible offer tailored to the needs of any company – no matter how long it has been in business, what industry it is in, or what form of business it has. Everyone will find something to suit their needs.
- No unnecessary paperwork. Thanks to the digital process, you will fill out the factoring application wherever you are now!
- A personalized caregiver who will support you at every stage of the contract, if necessary.
- Many years of experience – on the market since 1996!
- Additional benefits for regular customers.
Factoring in Poland
Factoring is still a relatively young service on the Polish market. The first factoring company began operations in 1994. The biggest challenge in the beginning, of course, was education. Helpful in spreading knowledge of factoring was to be the creation of the Confederation of Factoring Institutions, which was replaced in later years by the Polish Factors Association.
These measures have proven to be effective. Why? Because factoring has been gaining popularity over the years. In 2015, factoring was used by approx. 12,500. companies. This compares with more than 21,000 in 2020. entities.
It is worth noting at this point that PragmaGO already serves 15% of factoring clients in Poland. Looking at the growth rate, it can be assumed that factoring in Poland is just gaining momentum and will become even more popular over the next few years.
Factoring vs. other sources of corporate financing
There are many sources of business financing available. Among these externals, loans and credit remain the most popular. Nevertheless, factoring is gaining in popularity. It is useful to know the key differences between credit, leasing and factoring.
Basic differences between factoring and credit:
- Verification of creditworthiness and liquidity – in the case of factoring, counterparties are verified, while in the case of a loan, the company applying for financing is verified. Having temporary financial problems, but at the same time working with reliable contractors, we should easily get factoring. The bank, in turn, will most likely deny the loan.
- Speed of decision and access to funds – factoring can be obtained even in a few hours. A loan, on the other hand, involves a long wait for a decision and the provision of a large list of documents.
- Costs – interest rates for a loan are usually lower than those for factoring.
- Additional services – many factories also offer additional services like accounts receivable insurance and debt collection. When deciding on a loan, we have no such options.
Factoring vs. leasing
The answer to the question of which is better – factoring or leasing – should depend on what the company wants to use the obtained funds for. Factoring is worth opting for when a company needs funds to pay current obligations or when the deadline for payment of receivables is distant. Leasing, on the other hand, is worth choosing when a company needs cash to purchase fixed assets.
Factoring vs. assignment of receivables
Let’s start at the beginning, which is what an assignment of receivables is in general. This is nothing more than the transfer of the right to the claim to a third party called the assignee. The assignor, in turn, is called the person selling the claim in question. As factoring is a service involving the sale of invoices, the assignment agreement is crucial here. This is because the factor at the time of the sale of the invoice transfers all rights to it to the factor. However, the matter is not so simple due to the existence of different types of factoring.
How to account for factoring?
Accounting for factoring may seem complicated. All primarily because the process differs depending on the type of factoring chosen.
Since full factoring can literally be treated as if it were a sale of receivables, the amount due in this case should be included in financial income. The financing costs, in turn, can be “rolled into the costs” of doing business.
In the case of incomplete factoring, the factor is responsible for any insolvency of the recipient. In the accounting books, this type of service should be booked in the same way as in the case of a loan or credit.
This is just a very abbreviated description of what the factoring accounting process looks like. You can learn more here.
Factoring facts and myths
In this section, we will dispel the myths you may often encounter and confirm the facts.
Myth #1 – The most common myth about factoring is that the service is expensive and often fares worse than a loan. In fact, the prices of both services are comparable. Moreover, given that factoring is often accompanied by additional services, it is often more cost-effective than a bank loan.
Myth #2 – Factoring is the same as debt collection. Yes, in many cases the factor assumes the risk of the counterparty’s insolvency, but factoring itself is not a service to collect overdue receivables.
Myth #3 – Only large companies with a history can benefit from factoring. Factoring can be used by anyone. Non-bank factoring is primarily aimed at SME owners. It is worth remembering that in factoring, the counterparty, not the factoring company itself, is subject to verification, so even a new company has a chance to obtain financing, as long as it works with reliable business partners.
With all this in mind, it remains for us to wish you make the right choice and make the best business decisions in the future. When deciding on factoring, be sure to check out online factoring from PragmaGO and micro fact oring prepared with smaller companies in mind.


