What is the cost of the factoring service?
Factoring companies and banks offer factoring services of varying scope, but also at very different prices. Sometimes services that are similar at first glance turn out to be priced at completely different levels. The discrepancies in the fee tables of individual factoring companies are due to the fact that each company may assess risk differently, have a different financial policy or focus on a different target group.
What is taken into account when determining the final factoring price?
How much you will pay for factoring is based on many factors. What matters is the type of factoring, the industry in which you and your customers operate, the amount of advance payment you make, the typical payment terms with which you issue invoices, your company’s credit history, as well as the course of negotiations and individual arrangements between your company and the service provider.
How does the type of service affect the actual cost of factoring?
The available factoring variants differ in the activities that the factor must perform as part of their service, as well as the level of risk borne by the service provider.
It is for this reason that if you check how much full factoring (without recourse) costs , it will certainly turn out to be more expensive than incomplete factoring (with recourse). In the former, the factor assumes the risk of the counterparty’s insolvency – so if the recipient does not pay on time, the factor will be forced to carry out collection activities. The risk of such a situation is offset by higher commissions in full factoring.
The difference will also be clearly visible if we compare domestic factoring with international factoring. The latter will be more expensive, as the factor has to take into account fluctuating foreign currency exchange rates, higher costs of insuring the receivables, as well as the additional activities it has to perform in order to properly handle the factoring.
How does the factoring industry and its customers affect the price of factoring?
Once again, the reason is risk. In some industries the probability of unforeseen circumstances is clearly higher than in others. Some industries face an almost systemic problem of late payments, while in others the difficulty is overly complex or dynamically changing regulations. In such cases, the factor often decides to prepare a detailed financial analysis of the potential client before providing financing.
This does not mean, however, that representatives of more strongly risk-laden industries cannot use factoring. However, they must reckon with the need to provide additional collateral or higher costs for the service.
Reliability and timeliness of customers vs. cost of factoring
A company that wants to use factoring undergoes an analysis before financing is granted. More important to the factor, however, is the reliability and timeliness of its buyers. Ultimately, it is these companies that will repay the receivables to the factor’s account. So if the recipients have an extensive history of unpaid debts or have run into financial trouble in the past, the factor may refuse financing. In a borderline situation, however, it may offer higher costs or stipulate that it will provide financing, but without being able to assume the risk of insolvency.
Negotiate factoring for yourself
Negotiation is at the core of any business operation and its potential should not be underestimated. Regardless of the factors mentioned above, it is worth taking advantage of the opportunity to negotiate the terms of the contract. In this way, you can significantly reduce the price or – while keeping the one agreed before – acquire additional services.
Factoring costs and fees
If you want to calculate exactly how much factoring costs, you need to take into account many types of fees. Some of them are specific to bank factoring, some of them are only found in non-bank factoring, and some of them you have to reckon with regardless of who the factoring service provider is.
Below we describe what types of fees appear both in banks and in the price lists of non-bank factories. You will learn their exact values by checking the fee schedules of each service provider.
Preparation fee
Also referred to as an initial fee, preparation fee or factoring limit fee. As part of this fee, the factor prepares:
- An assessment of the financial situation of the factor and recipients,
- documents needed to conclude the agreement,
- valuation,
- security analysis.
The preparation fee is usually charged once at the conclusion of the contract. However, keep in mind that you may also have to pay an initial fee when extending your cooperation for another period. This is because the drafting of a new contract requires a number of steps to be carried out again, such as a financial analysis of the service recipient and its suppliers.
Charge for unused limit
An extremely important part of the factoring agreement is to determine the appropriate factoring limit for your company. Factors provide limits in different amount ranges, but a higher limit is not always beneficial to the factor – as the factor may charge a fee for the unused limit. This is due to the need to set aside funds in an appropriate amount for the use of the factor during the term of the contract.
The fee for an unused limit is also sometimes called a commitment fee.
Fee for exceeding the limit in concentration
Companies that chose to set too small a limit at the beginning of the contract may also face additional fees. Exceeding the limit in concentration can have two consequences: withholding financing or charging an overlimit fee.
This fee is also sometimes referred to as a contract limit increase fee. The principle is similar – payment of this fee means receiving additional funding under the same factoring agreement.
Important!
If your company uses factoring and its needs are growing, you can apply to the company providing the service for an increase in the factoring limit. Although the new limit will not be granted free of charge, the terms of the limit increase obtained through this route will certainly be more favorable than having to pay an overdraft fee.
Fee for assumption of risk
Factors charge additional fees for assuming the risk of insolvency of your company’s counterparty – an additional safeguard in case of repayment problems on the part of your customers. Such a fee generally ranges from 0.2% to 0.5% of the invoice value.
Remember that assumption of insolvency risk is an additional service. You do not have to use it, so the risk assumption fee is fully optional.
Fees for collection activities
As part of the factoring agreement, the factoring company may wish to use additional collection services provided by the factor should the need arise. In that case, it will be necessary to pay for collection activities, such as drafting and delivering calls for payment, attempting to contact debtors, and even court collection.
Insurance
Factors offer various types of additional insurance designed to give factoring companies peace of mind in the event of unforeseeable circumstances. As a rule, each of these insurances requires an additional fee. Some factories also offer free insurance.
Factoring – other fees
In addition to the fees mentioned above, some of the factories may also charge additional small fees, among them:
- Fee for changing the account number for billing,
- The fee for drafting another annex to the agreement,
- early termination fee.
If the payee delays repayment, the factor may also demand a late fee.
Important!
All of the fees described above should be duly described in the factoring agreement, so that factoring clients have no problem understanding what types of fees may apply to them both at the conclusion of the agreement and during its term.
Before you accept the terms of the contract, make sure you carefully read the fee schedule, attached by the factor to the document. If some of the items raise your doubts, ask the supervisor for more information.
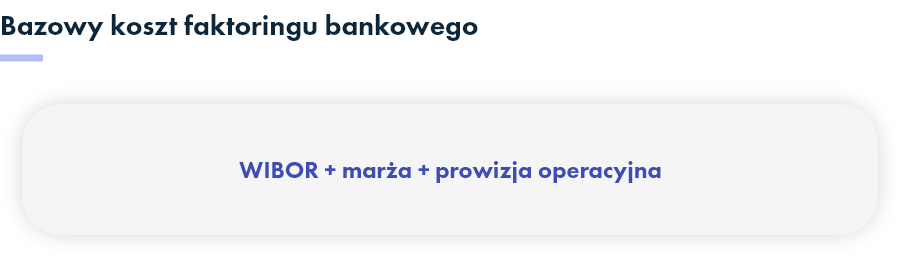
Basic costs of bank factoring
A sizable portion of the factoring market in Poland is that provided by bank factors. Their method of calculating the cost of the service consists of three elements: WIBOR, margin and commission.
WIBOR, or Warsaw Interbank Offered Rate, is the interest rate on loans in the interbank market. What interest rate a bank will lend money at will largely determine the cost of financing for the end customer. This also applies to factoring. The WIBOR parameter is set for specific periods, such as one day, one month, three months or six months. Bank factors usually include WIBOR 1m or 3m in calculating factoring costs.
Margin (or interest) is the term most commonly used in commerce. Represents the difference between the purchase price and the selling price. Although loans or factoring are not commodities, banks also need to make money on them, which is why they apply a margin. The basic margin is most often set at between 0.2% and 3% per month. How much interest will be for factoring in a given variant is a matter for each bank individually.
The operating commission, in turn, is charged on the amount of the invoice. The second factor that affects the commission is the due date of the invoice. Many bank factories (but non-bank factories as well) offer separate thresholds for invoices with 30-day, 60-day or 90-day payment terms. Similarly: the faster the repayment, the lower the cost for the factor.
EXAMPLE
With an invoice of PLN 100,000.00, the current WIBOR interest rate, and assuming the invoice is paid within 30 days, the interest will be PLN 388.08. To this must be added a commission. In the case of a factor charging a commission of 2%, the company will pay PLN 2,000.00. The total cost of factoring for the example given is PLN 2,388.08.
How much does non-bank factoring cost?
From the point of view of the end customer, a slightly friendlier form is taken by the costs of factoring offered by non-bank factors. Here we are usually dealing with a single commission, usually called a factoring commission. It is given on a monthly basis. This method of billing is more transparent, since the factoring company can accurately count the basic cost of the factoring service it will face during the term of the contract at the initial stage.
Non-bank factories also offer the inclusion of an essential cost in the form of a monthly commission expressed not as a percentage but as an amount – a flat rate, also known as a subscription rate.
The base cost of non-bank factoring consists of the factoring fee alone.
Transparent structure
Many entrepreneurs interested in factoring value the transparency of fees above all else. It is for this reason that non-bank factor offers are slightly more popular – they are characterized by greater flexibility in accessing additional services.
In addition, a transparent approach to factoring fees results in customers making more informed decisions about factoring agreements, which in turn has a positive impact on subsequent cooperation between factor and factor.
Factoring offers available to all
It is worth noting that the non-bank sector does not disqualify companies that have been on the market for a short time or have temporary financial problems or overdue receivables.
If the factoring company operates in an industry where deferred payment settlements of up to 90 or even 120 days are common, online factoring may prove to be a tool that will put an end to the company’s recurring liquidity problems. This, and the fact that the use of factoring does not increase the company’s debt, is particularly important for companies with short tenure and those with other liabilities.
While it is difficult to determine exactly what the cost of factoring may be without providing details, the calculator available on our site will show you an approximate cost, close to the final cost. You can find out the details by submitting a non-binding application. In response, you will receive a specific offer prepared individually for your company.


