Advance payment invoice – when should it be issued?
The structure and design of an advance invoice, as well as a list of situations in which the seller is required to issue such a document, are regulated by the Value Added Tax Law (usually referred to simply as the VAT Law). Art. 19a para. 8 of the same indicates that tax liability arises with the receipt of all or part of the payment. This means that already the receipt of an advance payment or down payment results in tax liability, but this only applies to VAT – we will return to this topic later.
Thus, if the buyer for whom you are providing a service or to whom you are selling goods is engaged in business, the down payment should not just be the subject of a verbal agreement. The mere mention of an advance payment in the written contract entered into by the parties is also not enough. You – as the seller – are obliged to document the advance received with an advance invoice.
Important!
There are several exceptions to this rule – an advance invoice does not need to be issued in situations specified by the law – for example, when the subject of the contract is:
- The supply of electricity, heat, refrigeration or line gas;
- Distribution of electricity, heat, refrigeration or line gas;
- Telecommunications or radio communication service;
- The service of treating or supplying water through waterworks;
- Rental, lease or rental service;
- Security service for persons, property, guarding or storage;
- Legal or office services.
How to issue an advance invoice?
The components of an advance invoice are also detailed in the VAT Law, specifically in Art. 106e and 106f. What data must appear on an advance invoice?
- date of issuance of the advance invoice;
- a consecutive number assigned within one or more series that uniquely identifies the invoice;
- The names or surnames of the taxpayer and the purchaser of goods or services and their addresses;
- the number by which the taxpayer is identified for tax purposes (NIP, REGON or PESEL in the absence of the first two);
- the date on which the delivery of goods or performance of services was made or completed, or the date on which payment was received, if such date is specified and differs from the date of invoice;
- payment amount received;
- tax amount calculated according to the formula:
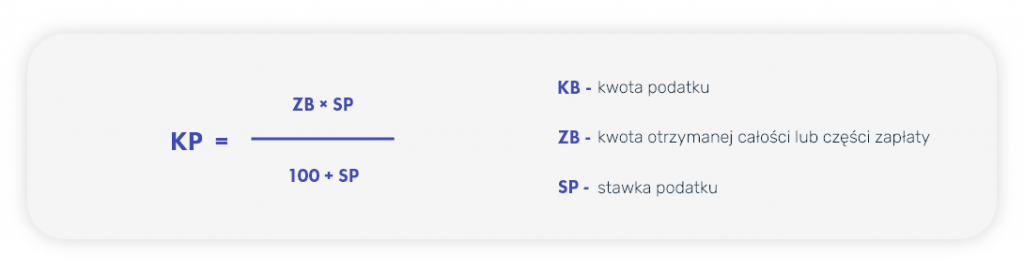
- Data on the order or contract, in particular:
- Data on the order or contract, in particular:
- The name or type of goods or services;
- Quantity of goods ordered;
- The value of the goods or services ordered without the amount of tax;
- Tax rate;
- Tax amount;
- The value of the contract or agreement including the amount of tax.
Important!
The deadline for issuing an advance invoice should coincide with generally accepted invoicing rules – so the seller is obliged to issue such a document no later than the 15th. day of the month following the month of receipt of part or all of the payment. An advance invoice can also be issued in advance, but not more than 60 days.
Blank VAT invoices
However, issuing advance invoices in advance carries certain risks. It is likely that the advance invoice issued by the seller well in advance will not be paid within the statutory deadline. Such a ruling is particularly unfavorable precisely for the seller, because it means that the invoice issued by him does not refer to the actual transaction, and thus it will be classified as a so-called “invoice”. “blank invoice.”
Blank VAT invoices should not be included in the JPK return (and at the same time, the entrepreneur is obliged to include any advance invoice issued in the return). This is mentioned in Art. 88 para. 3a pt. 4(a) of the VAT Law.
EXAMPLE
Mr. Leon issued an advance invoice to a contractor on October 11 and included it in the JPK_V7 declaration for the accounting period. However, 60 days have passed, and the down payment has still not been made. Henceforth, the invoice qualifies as an empty invoice, since it does not refer to the concluded transaction – so it is suspected that the buyer may have wrongfully deducted VAT on the transaction. Mr. Leon’s solution is to immediately withdraw the advance invoice from circulation as soon as the statutory 60 days that the buyer has to pay have passed. If he fails to do so, he exposes himself to criminal and fiscal consequences.
For issuing empty VAT invoices, entrepreneurs face consequences detailed in the Fiscal Penal Code, specifically in Art. 56 § 1:
A taxpayer who, when submitting a declaration or statement to a tax authority or payer, gives untruth or conceals the truth or fails to fulfill the obligation to notify of a change in the data covered by them, thereby exposing the State Treasury or a local government unit to a tax loss, shall be subject to a fine of up to 720 daily rates or imprisonment for up to 2 years, or both.
Subsequently, the law specifies additional conditions that take into account the small value of the depleted tax (in which case the entrepreneur faces only a fine of up to 720 daily rates) or even an amount that does not exceed the statutory threshold (in which case the highest consequence may be a fine for a fiscal offense).
The seller should therefore remember that if the buyer withdraws from the transaction or otherwise fails to pay before 60 days, the advance invoice should be immediately withdrawn from circulation.
How to account for an advance invoice?
However, let’s assume that everything went smoothly – we issued an advance invoice and the contractor fulfilled his promise. In such an arrangement, it is worth remembering that the advance invoice is booked only for VAT – once the advance invoice is issued and the advance payment is received in the company’s account, there is no need to pay PIT. The obligation to pay income tax for this transaction will arise only after the final invoice, a document that, so to speak, supplements the advance invoice.
Important!
Such a situation, as described above, occurs only when the advance invoice covers only part of the payment for the performance of a service or delivery of goods.
The buyer should also pay attention to the timing of settlement of the advance invoice – especially if he received the advance invoice before the payment was made. The mere receipt of a prepayment invoice does not give rise to VAT tax liability – it is only the payment of part or all of the amount that allows the buyer to deduct VAT. Special attention should be paid to this if the seller has issued an advance invoice at the end of a given accounting period, and the advance payment is already made in the following period.
Final invoice to advance invoice
In most cases, issuing an advance invoice does not end the matter – it is also necessary to issue a final invoice to the advance invoice. What should you know about the final invoice?
When is a final invoice issued?
We issue a final invoice when the advance invoice included only a part of the amount to be paid for the goods delivered or services performed. So if, for example, we issued an advance invoice for 30% of the agreed amount (and such payment was received into the company account), the final invoice should show the missing 70% of the value of the service or goods.
How do I post the final invoice to the advance invoice?
As we mentioned earlier, the issuance of a prepayment invoice triggers a tax liability – but this is only for VAT. Income tax should be paid only after the final invoice is issued.
EXAMPLE
Ms. Maja issued an advance invoice for the net amount of PLN 3,000. This represents 30% of the value of the service. She received an advance payment of PLN 3,690 from her contractor. The entrepreneur then books the advance invoice in JPK_V7 and pays the VAT on it, which is PLN 690. After the service is completed, Ms. Maja issues another document – a final invoice. It shows a net amount of PLN 7,000 (that is, the missing 70% of the amount). The buyer pays PLN 8,610, and Ms. Maja is required to pay PLN 1,610 in VAT and PLN 1,900 in income tax (since she is on a flat tax) in a given accounting period.
When is a final invoice not necessary?
There are also situations in which the seller issues an advance invoice that takes into account 100% of the amount to be paid. Such a document is called an advance-final invoice. After issuing an advance-final invoice, there is no need to issue a separate final invoice (since all of the costs have already been taken into account), but the payment must then be recorded in both value-added tax and income tax.


